2025 Nobel Prize | Defining the Molecular Basis of Self–Non-Self Recognition in Immunity

On October 6, 2025, American scientists Mary E. Brunkow, Fred Ramsdell, together with Japanese scientist Shimon Sakaguchi, were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize for their discovery of regulatory T cells (Tregs) and the mechanisms of peripheral immune tolerance. Their pioneering work addressed a central question in immunology: how the immune system avoids attacking self tissues while mounting effective responses against pathogens.
Three Major Breakthroughs: From the Discovery of the Cell Type to a Complete Mechanistic Framework
01. Identifying the “Safeguards” Within T Cells
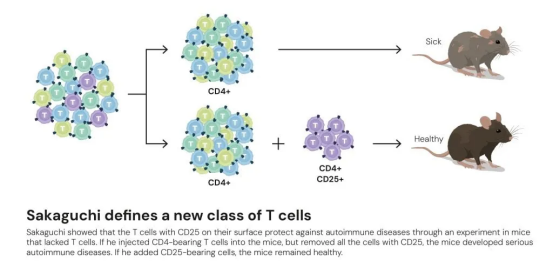
In 1995, Shimon Sakaguchi demonstrated that transferring healthy, mature T cells into diseased mice lacking a thymus could reverse autoimmune pathology. This pivotal observation led to the identification of a distinct subset of T cells in the peripheral immune system—regulatory T cells (Tregs). These cells suppress excessive immune activation and prevent misguided attacks on self tissues. The discovery fundamentally overturned the long-held view that immune tolerance relies solely on thymic selection.
02. Identifying the Key Gene Behind “T-Cell Rebellion”
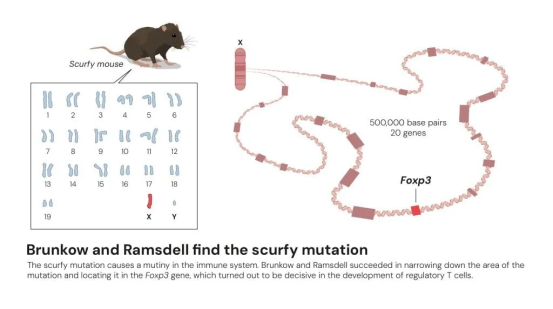
In 2001, Mary E. Brunkow, Fred Ramsdell, working with mouse models of autoimmune disease, identified mutations in the FOXP3 gene on the X chromosome as the cause of severe immune dysregulation, in which T cells indiscriminately attack self tissues. They further demonstrated that FOXP3 mutations give rise to a rare and often fatal autoimmune disorder known as IPEX syndrome.
03. Establishing the Complete “Cell–Gene” Regulatory Framework
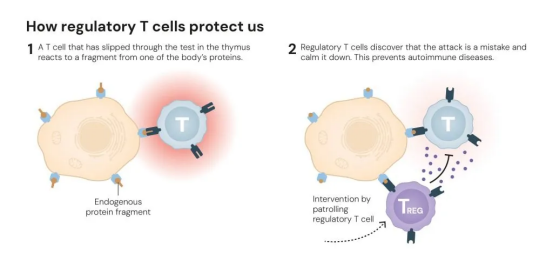
In 2003, Shimon Sakaguchi and his team demonstrated that FOXP3 functions as the molecular “master switch” for Tregs. Loss of this gene abolishes Treg development and leads to widespread autoimmune disease. Their work established the framework of peripheral immune tolerance, showing that Tregs, under FOXP3-mediated regulation, precisely maintain immune homeostasis.
T-cell culturing
For routine T-cell culture, boosting proliferation, persistence, and function—especially in suppressive TMEs—relies heavily on cytokines. IL-2, IL-7, and IL-15 are the core trio, with IL-12 as an auxiliary factor.
IL-2 mainly drives effector T cells (Teff), which are potent killers but prone to terminal differentiation and exhaustion, limiting their persistence. In contrast, IL-7/IL-15 favor memory T cells (Tmem, especially Tcm), offering stronger proliferative capacity, lower exhaustion, and better in vivo durability—traits ideal for adoptive cell therapy.
How to Mix Growth Factors for Different Culture Scenarios?
Research Setting
If the goal is simply to achieve robust T-cell expansion, a combination of high-dose IL-2 with a small amount of IL-12 is sufficient. High-dose IL-2 delivers strong proliferative signals, driving rapid expansion and effector molecule production. Early IL-12 exposure polarizes the T-cell response toward a potent Th1/CTL phenotype, yielding a higher proportion of IFN-γ⁺ and granzyme B⁺ effector cells.
Solid Tumor Setting
Given the complexity of the tumor microenvironment, the IL-7 + IL-15 combination is commonly used. This pairing maximizes the generation of stem-like memory T cells and central memory T cells. These subsets are long-lived, self-renewing, and capable of robust recall expansion upon antigen encounter—making them essential for achieving durable responses in solid tumor therapy.
CAR-T Therapy Setting
A common combination is IL-2 + IL-7 + IL-15. IL-2 provides strong effector function and expansion capacity, while IL-7 and IL-15 help maintain a pool of memory T cells after the initial effector wave—supporting long-term disease control and reducing the risk of relapse.
Inducing Regulatory T Cells
The IL-2 + TGF-β combination is used, where TGF-β is the key driver that induces naïve T cells to differentiate into regulatory T cells, and IL-2 is essential for T-cell proliferation and Treg maintenance.
Growth factors are the core blueprint of successful T-cell culture. Selecting the right cytokines, optimizing their ratios, and fine-tuning their concentrations are essential to cultivating T cells that grow stronger, last longer, and perform with greater potency.
At EastMabBio, we are dedicated to delivering cytokines of uncompromising quality. Guided by a rigorous quality management system, we have developed a comprehensive portfolio of GMP-grade cytokines designed specifically for T-cell culture and advanced cell-therapy development. As innovation accelerates, new and more powerful cytokine combinations will continue to emerge—and EastMabBio will remain at the forefront, empowering next-generation immunotherapies.
Product Recommendations
Cat# | Name | Species | size | Purity | Endotoxin (EU/mg) | Expression System |
Y02001 | IL-2 | Human | 100µg/1mg | ≥95% | ≤1 | CHO |
Y02401 | IL-7 | Human | 10µg/50µg/1mg | ≥95% | ≤10 | CHO |
Y02701 | IL-15 | Human | 10µg/50µg/1mg | ≥95% | ≤10 | CHO |
Y04001 | IL-12 | Human | 10µg/50µg/1mg | ≥95% | ≤10 | CHO |
Y02901 | IL-21 | Human | 10µg/50µg/1mg | ≥95% | ≤10 | CHO |
Y02201 | IL-4 | Human | 10µg/50µg/1mg | ≥95% | ≤10 | CHO |
Y01801 | IFN-γ | Human | 10µg/50µg/1mg | ≥95% | ≤10 | CHO |
Y01821H | IFN-γ | Human | 10µg/50µg/1mg | ≥95% | ≤10 | E.coli |
Y04201N | TGF-β1 | Human | 10µg/50µg/1mg | ≥95% | ≤10 | CHO |
For product details and datasheets, please email us at product@eastmabbio.com or call +86 400 998 0106.
References
1. IL-2 regulates perforin and granzyme gene expression in CD8+ T cells independently of its effects on survival and proliferation. J Immunol. 2005.
2. IL-7 and IL-15 differentially regulate CD8+ T-cell subsets during contraction of the immune response.Blood. 2008.
3. Adoptive immunotherapy for cancer: harnessing the T cell response.Nat Rev Immunol. 2012.
4. Cutting edge: TGF-beta induces a regulatory phenotype in CD4+CD25- T cells through Foxp3 induction and down-regulation of Smad7.J Immunol. 2004.
News
-
 NewsHonor | East-Mab Bio Biotech won the title of "Excellent Partner of Biochemical and Biological Enterprises"2023.12.29
NewsHonor | East-Mab Bio Biotech won the title of "Excellent Partner of Biochemical and Biological Enterprises"2023.12.29 -
 NewsExhibition Invitation | East-Mab Bio Biotech "Yu" Meets You at CACLP2024.03.11
NewsExhibition Invitation | East-Mab Bio Biotech "Yu" Meets You at CACLP2024.03.11 -
 NewsEast-Mab Bio | The 9th Cell Biology Industry Conference will meet you in March2024.02.26
NewsEast-Mab Bio | The 9th Cell Biology Industry Conference will meet you in March2024.02.26



